#include <MNRTPSinkSH.h>
Inheritance diagram for SH::RTPSinkSH:

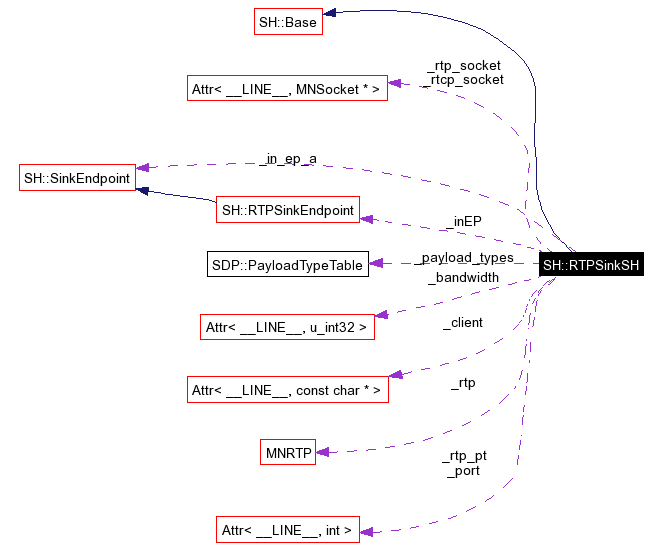
Public Member Functions | |
| RTPSinkSH (SHGraphManager *mgr, u_int32_t runtimeId, MNSelector &sel, RTSP::TransportTypes req_transport=RTSP::RTP_AVP_UDP) | |
| virtual | ~RTPSinkSH () |
| virtual SH_RC | initSH () |
| virtual SH_RC | uninitSH () |
| virtual SH_RC | startStreaming () |
| virtual SH_RC | stopStreaming () |
| SH_RC | push_to_net (DataPtr item) |
| virtual void | pushReport (ReportPtr report, Direction d) |
| virtual u_int16 | get_rtp_seq () |
| virtual u_int32 | get_rtp_time () |
| virtual u_int32 | get_ssrc () |
| void | set_payload_types (const SDP::PayloadTypeTable *ptt_ptr) |
| virtual SinkEndpoint ** | getSinkSpecs () |
| virtual SourceEndpoint ** | getSourceSpecs () |
| virtual bool | isConnected () const |
Public Attributes | |
| SA_RTPSNK_RTP_SOCK_PORT | _rtp_socket |
| SA_RTPSNK_RTCP_SOCK_PORT | _rtcp_socket |
| SA_RTPSNK_CLIENT_NAME | _client |
| SA_RTPSNK_CLIENT_PORT | _port |
| SA_RTP_BANDWIDTH | _bandwidth |
| SA_RTP_RTP_PAYLOAD_TYPE | _rtp_pt |
| const SDP::PayloadTypeTable * | _payload_types |
Protected Attributes | |
| SinkEndpoint * | _in_ep_a [1] |
| RTPSinkEndpoint | _inEP |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reimplemented from SH::Base.
|
|
|
Reimplemented from SH::Base.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provide a list of valid sink endpoint specifications to the graph manager.
Implements SH::Status.
|
|
|
Provide a list of valid source endpoint specifications to the graph manager.
Implements SH::Status.
|
|
|
Reimplemented from SH::Base.
|
|
|
Indicate whether a sufficient number of endpoints are connected for the stream handler to be active. Implements SH::Status.
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
pushReport(r) can be called on source and sink endpoints, which will in turn call their owning stream handler for forwarding the report into the same general direction. The specific stream handler must overload this call if it wants to evaluate the reports, or if it has downstream or well as upstream endpoints. If the SH does not care about reports and has endpoints on only one side, it needs not overload this function. The reports are ignored and deleted in that case. Reimplemented from SH::Base.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reimplemented from SH::Base.
|
|
|
Reimplemented from SH::Base.
|
|
|
Reimplemented from SH::Base.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See _rtp_port. In case that a pair of UDP sockets is given, the RTCP socket is held by _rtcp_socket. |
|
|
|
|
|
The sending RTP socket must now be given as an open UDP socket. |
 1.3.8
1.3.8